
In recent years, the mining industry has been facing increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact and embrace sustainable practices.
“Extractive industries are responsible for half of the world’s carbon emissions and more than 80% of biodiversity loss”
“Resource extraction responsible for half world’s carbon emissions”, The Guardian, 2019
As governments and regulatory bodies focus on reducing emissions from Non-Road Mobile Machinery (NRMM) engines, the mining sector finds itself at a critical crossroads.
The implementation of the NRMM Regulation, which sets emission limits for NRMM engines based on their power ranges and applications, is reshaping the industry’s landscape and driving the need for alternative propulsion systems. One such solution that holds immense promise is the advent of electric mining vehicles.
Despite the industry’s recognition of the benefits of electrification, the transition has been slower compared to other sectors. This article explores the challenges and complexities associated with the electrification of mining vehicles.
Why is the electrification of the mining industry so challenging?
The mining industry’s journey towards electrification presents a unique set of challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation. As mining companies seek to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace sustainable practices, transitioning from conventional fossil fuel-powered vehicles to electric mining vehicles becomes a compelling option.
However, several critical factors contribute to the complexity of this transformation. This chapter delves into the challenges faced by the mining industry in electrifying its operations, focusing on three key aspects: variation of temperatures, energy storage capacity requirements, and the need for adequate charging infrastructure.
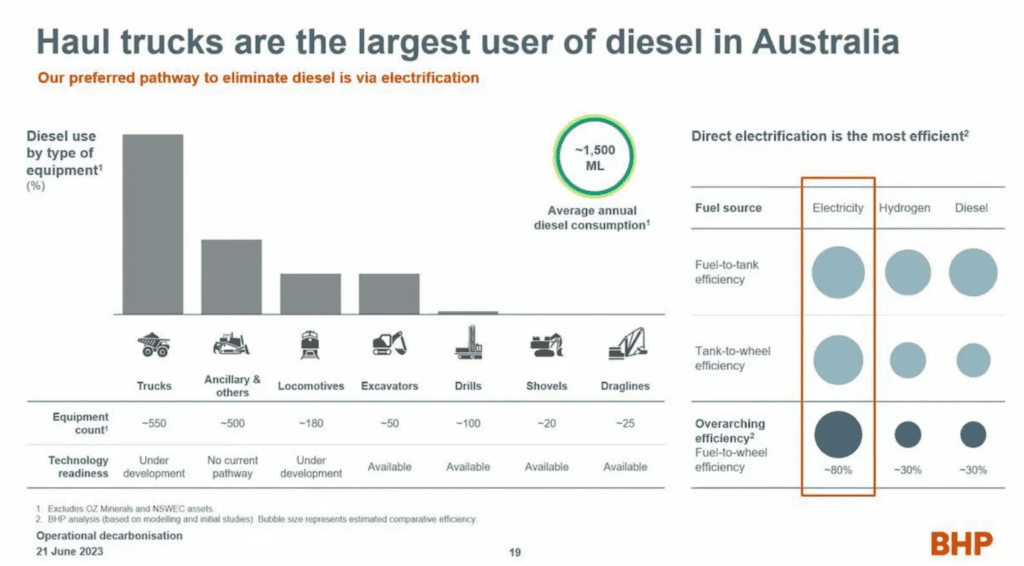
The challenges of electrification are indeed significant when considering that 30% of the expenses of a mining company are related to diesel consumption.
Variation of Temperature
Mining operations often take place in diverse and demanding environments, subjecting equipment to extreme temperatures and harsh conditions.
From freezing cold climates to scorching heat, the variations can pose significant challenges for electric mining vehicles.
Batteries, a crucial component of electric vehicles, can experience reduced performance and efficiency under extreme temperatures. Ensuring the reliable and optimal functioning of batteries in such challenging conditions necessitates the development of specialized battery technologies and thermal management systems.
Requires a Certain Energy Storage Capacity
Mining vehicles are typically heavy-duty machines designed to operate under strenuous conditions, demanding substantial power and energy.
To match the performance and endurance of conventional diesel-powered counterparts, electric mining vehicles require a certain energy storage capacity.
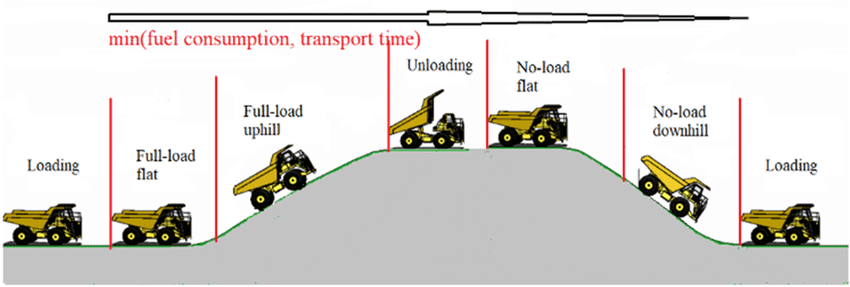
A very demanding haul cycle. Source : Implementation of velocity optimization strategy based on preview road information to trade off transport time and fuel consumption, Research Gate
To match the performance and endurance of conventional diesel-powered counterparts, electric mining vehicles require a certain energy storage capacity. Achieving this requires advanced battery technologies capable of storing and delivering sufficient energy for extended periods without compromising vehicle performance.
Enhancing energy density, durability, and overall battery efficiency becomes imperative to meet the demanding requirements of mining operations.
Requires a Certain Charging Infrastructure
An efficient and reliable charging infrastructure is fundamental for the widespread adoption of electric mining vehicles. However, establishing a comprehensive charging network in remote mining sites can be logistically challenging.
The need for robust charging infrastructure that can accommodate the high power demands of mining vehicles becomes essential.

Source: ABB develops Australian first for electric charging at CSA copper mine, ABB, 2022
Additionally, the charging process must be optimized to minimize downtime, as mining operations often operate on tight schedules. Developing solutions such as fast-charging technologies, decentralized charging stations, and intelligent grid integration are crucial to ensure the practicality and viability of electrifying the mining industry.
Immersion Cooling Thermal Management: a solution to these challenges
As the mining industry grapples with the challenges of electrification, innovative solutions are emerging to address the specific hurdles associated with temperature variations, energy storage capacity requirements, and charging infrastructure.
One such solution that shows immense promise is immersion cooling thermal management.
Resistance to extreme temperature variations
One of the primary concerns in mining operations is the ability of batteries to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations. Immersion cooling provides an effective solution by submerging the battery modules in a thermally conductive dielectric fluid.
This approach offers superior temperature regulation, ensuring that batteries remain within the optimal operating range even in harsh environmental conditions. By maintaining a consistent temperature, immersion cooling mitigates the risk of performance degradation and prolongs battery life, ultimately enhancing the reliability and efficiency of electric mining vehicles.
Immersion Cooling Enables Fast Charging
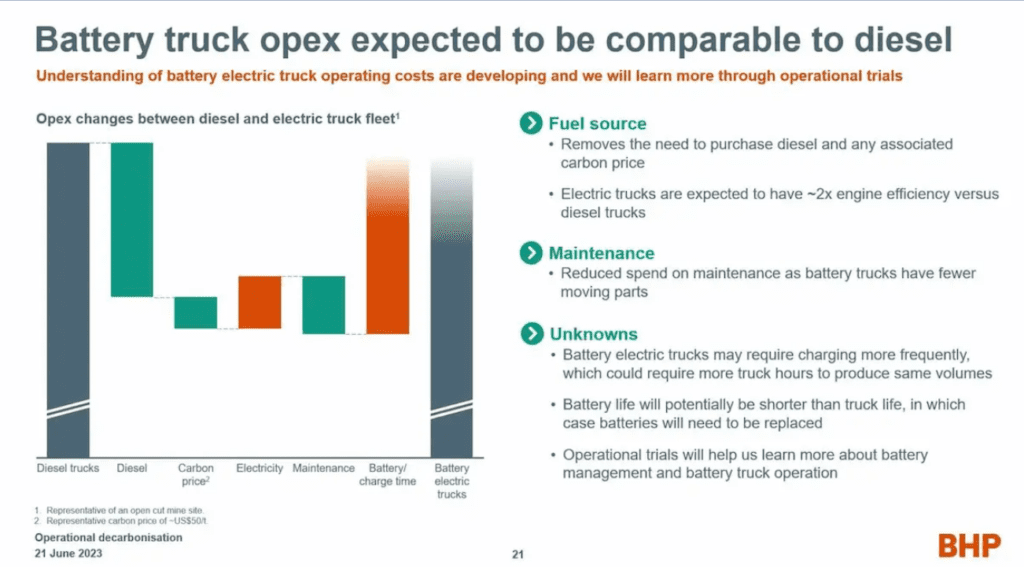
By immersing the battery modules in a thermally conductive fluid, heat generated during the charging process is dissipated more efficiently compared to traditional air-cooled systems.
This enhanced cooling efficiency allows for higher charging rates without compromising the battery’s integrity. As a result, mining operators can significantly reduce the charging time, enabling increased vehicle utilization and optimizing operational efficiency.
Safety, extended resistance and lifetime
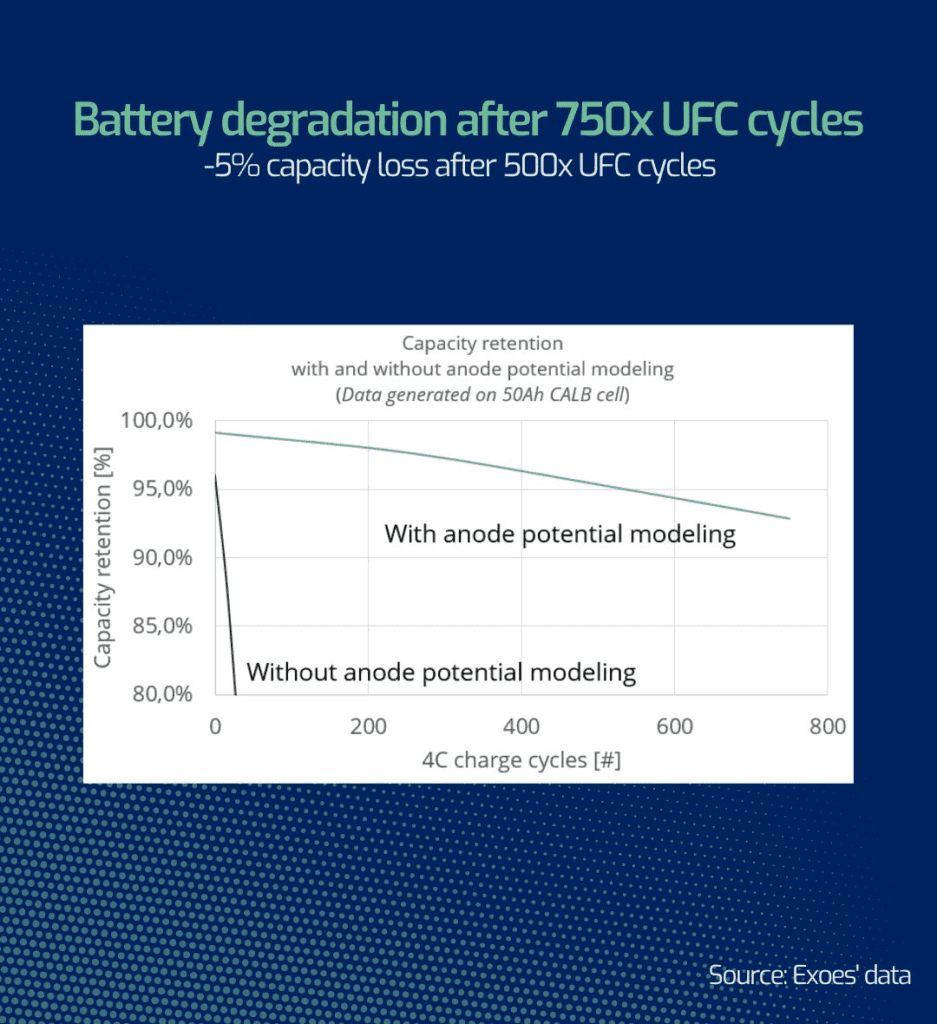
Beyond temperature regulation and fast charging capabilities, immersion cooling offers additional advantages for electric mining vehicles. The dielectric fluid used in immersion cooling systems also acts as a protective barrier, shielding the battery modules from external elements such as dust, moisture, and vibrations.
This added protection enhances the durability and longevity of the batteries, reducing maintenance requirements and overall operational costs. Furthermore, immersion cooling eliminates the need for complex air cooling systems, simplifying the design and reducing the weight and footprint of the thermal management system in mining vehicles.
To learn more about immersion cooling technology, please check out the replay of our latest webinar:

